buyNow
Temporary Power Market
Temporary Power Market Size, Share, Growth & Industry Analysis, By Fuel type (Diesel, Gas, Others), By Power Rating (Less than 80 kW, 81 kW-280 kW, 281 kW-600 kW, Above 600 kW), By End-use Industry, and Regional Analysis, 2025-2032
pages: 160 | baseYear: 2024 | release: July 2025 | author: Sunanda G.
Market Definition
Temporary power refers to rental or short-term electrical solutions used during emergencies, construction, events, or maintenance outages. It include generators, switchgear, transformers, and distribution equipment tailored for rapid deployment and flexibility.
The market serves industries such as construction, entertainment, disaster response, and utilities, where uninterrupted power is critical for safety and operational continuity. Applications include powering construction sites, ,planned shutdowns, supporting outdoor events, and emergency relief efforts.
Temporary Power Market Overview
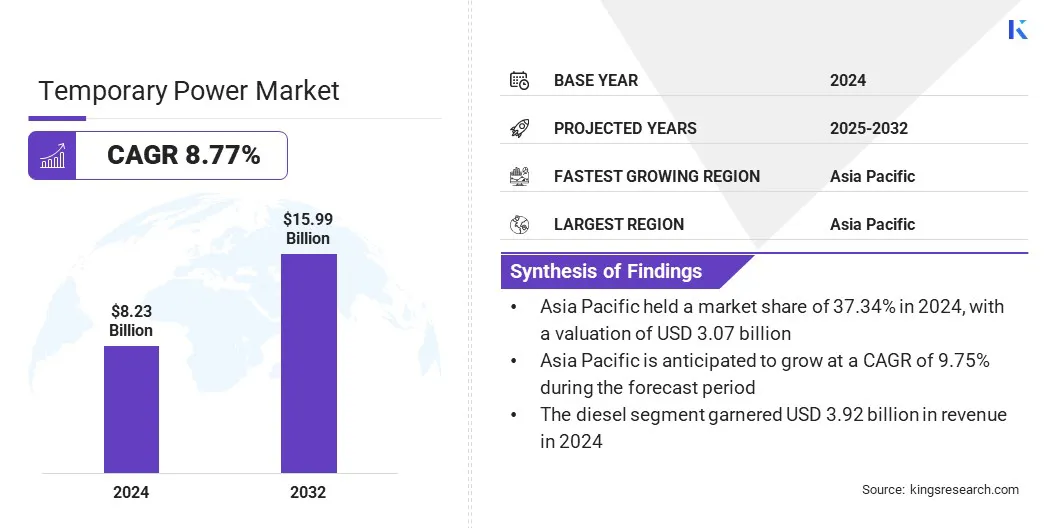
The temporary power market size was valued at USD 8.23 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 8.88 billion in 2025 to USD 15.99 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.77% during the forecast period.
Market growth is driven by the rising grid instability and frequent service disruptions that prompt industries to rely on backup solutions. Additionally, there is a notable shift toward cleaner energy options, with increased adoption of hybrid and renewable-integrated systems to reduce emissions and meet evolving sustainability goals.
Key Highlights
- The temporary power industry size was valued at USD 8.23 billion in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.77% from 2025 to 2032.
- Asia Pacific held a share of 37.34% in 2024, valued at USD 3.07 billion.
- The diesel segment garnered USD 3.92 billion in revenue in 2024.
- The 81 kW – 280 kW segment is expected to reach USD 6.00 billion by 2032.
- The utilities segment secured the largest revenue share of 36.54% in 2024.
- Europe is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.16% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the temporary power market are Aggreko, Cummins Inc., Caterpillar, APR Energy, Kohler Co., Atlas Copco Group, Generac Power Systems, Inc., Briggs & Stratton, Ashtead Group plc, YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD, ATCO Ltd., HIMOINSA, Doosan Bobcat, Wacker Neuson SE, and Speedy Hire Plc.
Rising number of large-scale construction and infrastructure projects is boosting demand for temporary power solutions. These developments often occur in areas without reliable or established grid access, prompting construction firms to use temporary power systems to operate heavy machinery, lighting, and essential site functions.
Such systems ensure uninterrupted operation, safety, and compliance with project timelines. Their flexible configuration enables adaptation to varied site requirements and power loads across different project phases.
- In June 2025, POWR2 introduced the POWRBANK MAX, a large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) designed for remote and off-grid construction and infrastructure sites. The system offers modular scalability and hybrid deployment, ensuring quieter, cleaner, and more reliable power in areas without grid access.
Market Driver
Grid Instability and Service Disruptions
Frequent power outages and scheduled maintenance are driving increased reliance on temporary power solutions across utilities and industries. Unstable grid conditions are prompting businesses to deploy backup systems to avoid operational downtime and protect critical processes. Rental generators and mobile power units are being used to ensure continuity during infrastructure repairs, natural disasters, and peak load periods.
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and data centers are adopting temporary power to maintain productivity and safeguard sensitive equipment. Utilities are also using these systems to support grid resilience and manage planned outages without affecting end users.
- Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) approved a USD 54 million plan to relocate 15 large mobile diesel generators from Houston to San Antonio during the summer. This move aims to address transmission bottlenecks caused by retiring gas-fired plants and rising demand due to renewable energy integration and infrastructure growth. The generators, with a combined capacity of around 450 MW, are expected to mitigate the risk of rolling blackouts while transmission system upgrades are underway.
Market Challenge
High Capital and Operational Costs
A key challenge limiting the expansion of the temporary power market is the substantial cost involved in procuring and maintaining generator fleets, managing fuel operations, and coordinating logistics. These expenses are particularly burdensome for smaller firms that lack the financial and operational scale to absorb such overheads.
High running costs and complex deployment requirements are reducing flexibility and slowing project execution in cost-sensitive sectors. To address this challenge, market players are offering rental-based models, fuel-efficient generator designs, and integrated service packages to reduce ownership and operational burdens. Companies are also streamlining logistics and implementing remote monitoring systems to enhance efficiency and lower total costs.
Market Trend
Notable Shift Toward Cleaner Solutions
A key trend influencing the temporary power market is the growing use of hybrid systems that combine conventional and renewable energy sources. Operators are deploying configurations that include gas generators, battery storage, and solar-diesel hybrids to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Battery integration supports load balancing and optimizes generator performance, while solar inputs reduce fuel dependency, particularly in remote or off-grid locations. This shift toward mixed-generation solutions reflects the efforts to meet temporary energy needs sustainably and cost-effectively.
- In January 2024, Hybrid Power Solutions Inc. introduced the Batt Pack Spark, a fuel-free mobile hybrid power unit comparable to a 25 kW diesel generator. This system incorporates a 28 kWh battery bank and supports up to 18 kW of solar input, enabling efficient load balancing. It operates across –30 °C to +50 °C, offering robustness for construction, military, mining, and jobsite applications.
Temporary Power Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation |
Details |
|
By Fuel type |
Diesel, Gas, Others |
|
By Power Rating |
Less than 80 kW, 81 kW – 280 kW, 281 kW – 600 kW, Above 600 kW |
|
By End-use Industry |
Utilities, Construction & Mining, Oil & Gas, Events & Entertainment, Others |
|
By Region |
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico |
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe | |
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific | |
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa | |
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America |
Market Segmentation
- By Fuel type (Diesel, Gas, and Others): The diesel segment earned USD 3.92 billion in 2024, mainly due to its high reliability, fuel efficiency, and widespread availability.
- By Power Rating (Less than 80 kW, 81 kW – 280 kW, 281 kW – 600 kW, and Above 600 kW): The 81 kW – 280 kW segment held a share of 38.78% in 2024, fueled by its optimal capacity range, making it highly suitable for a wide variety of mid-scale applications such as construction sites, small industrial operations, and commercial facilities.
- By End-use Industry (Utilities, Construction & Mining, Oil & Gas, and Events & Entertainment, and Others): The utilities segment is projected to reach USD 5.52 billion by 2032, owing to its critical need for reliable backup solutions during grid outages, maintenance operations, and peak load periods, ensuring uninterrupted power supply and system stability.
Temporary Power Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
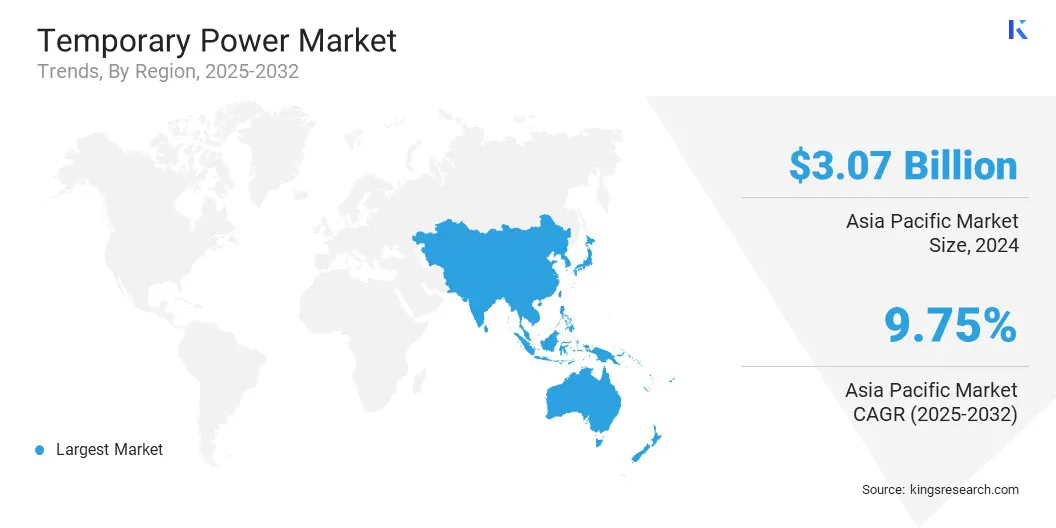
The Asia Pacific temporary power market share stood at 37.34% in 2024, valued at USD 3.07 billion. This dominance is attributed to the rapid industrial expansion across several Asia-Pacific countries, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, mining, and processing.
Countries such as India, China, Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines are witnessing strong growth in these industries, often in remote or underdeveloped areas where access to stable, permanent power infrastructure remains limited or unreliable.
To maintain continuous operations and avoid costly downtime, businesses in these regions are increasingly turning to temporary power solutions, including diesel and gas generators, hybrid systems, and battery-supported units, thereby fueling regional market growth.
- In April 2024, Aggreko introduced a mid-sized 500 kW / 250 kWh BESS tailored for temporary and hybrid power applications in industrial and construction sites across Asia-Pacific. The fully integrated, modular system supports both island mode and generator integration, ensuring reliable power in remote or off-grid locations.
The Europe temporary power industry is poised to grow at a CAGR of 9.16% over the forecast period. This growth is propelled by the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as floods, heatwaves, and winter storms. These events pose significant risks to existing power infrastructure.
In response, governments and utility companies are investing in temporary power solutions to enhance emergency preparedness and ensure rapid recovery. These systems are swiftly deployed in affected areas to restore essential services, making emergency backup power a critical and growing segment of the regional market.
- In June 2024, the European Commission activated its rescEU energy reserves, deploying over 1,000 power generators from EU strategic stockpiles to assist Ukraine’s critical power supply. These diesel and large-scale generators ensured continuity of essential services such as hospitals and heating centers, underscoring government investments in mobile backup power systems.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., temporary power systems such as diesel generators are regulated under the Clean Air Act by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Non-road engines must comply with Tier 4 Final emission standards, which require major reductions in nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter emissions.
- In the EU, temporary power systems are regulated by the Medium Combustion Plant Directive (Directive 2015/2193/EU), which sets emissions thresholds for plants with rated thermal input between 1 and 50 megawatts. Countries must transpose the directive into national laws. It requires registration, emissions monitoring, and reporting of generators, with stricter standards for plants operating in urban or high-density population areas.
- In Japan, the Ministry of the Environment enforces emissions regulations for generators under the Air Pollution Control Law. Temporary and permanent diesel generators must be certified based on output capacity and installation type. Regional Environmental Bureaus issue operational permits and set real-time emission limits for nitrogen oxides and particulates.
- South Korea’s Clean Air Conservation Act governs the use of temporary diesel generators and mobile power units. Generators must be registered with local environmental offices and are subject to particulate and nitrogen oxide emission limits. Equipment manufacturers must certify engine compliance with the Ministry of Environment standards.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the temporary power industry are focusing on strategies such as product innovation, advanced system integration, and strategic partnerships to maintain competitiveness. Companies are investing in R&D to develop compact, fuel-efficient, and easy-to-deploy solutions tailored for critical applications.
Firms are also collaborating with rental service providers and infrastructure developers to expand their reach and offer more flexible power solutions. These strategic efforts are helping companies respond effectively to changing customer demands and operational challenges across various end-use sectors.
- In June 2024, Cummins launched its Centum Force containerized generator sets, designed for temporary and critical power applications across data centers, manufacturing plants, hospitals, and construction/rental sites. These fully integrated systems include gensets, controls, switchgear, and remote monitoring capabilities.
Key Companies in Temporary Power Market:
- Aggreko
- Cummins Inc.
- Caterpillar
- APR Energy
- Kohler Co.
- Atlas Copco Group
- Generac Power Systems, Inc.
- Briggs & Stratton.
- Ashtead Group plc.
- YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD
- ATCO Ltd.
- HIMOINSA
- Doosan Bobcat.
- Wacker Neuson SE
- Speedy Hire Plc.
Recent Developments (Expansion/Product Launches)
- In October 2024, Generac Power Systems expanded production of portable and standby generators at its Wisconsin and South Carolina manufacturing plants in response to increased demand, fueled by a record 1.2 billion utility outage hours in the U.S. due to hurricanes and grid instability.
- In May 2024, Cummins launched the Centum Force containerized generator set at Data Centre World Asia in Singapore. The 40-foot, stackable unit offers turnkey power delivery for industrial and remote sites, supporting infrastructure development across the Asia-Pacific region.
- In July 2023, Atlas Copco introduced a mobile hybrid generator combining lithium-ion battery storage and a QAS+ diesel unit. The system reduces fuel use and CO₂ emissions, and noise in sensitive environments.
freqAskQues
